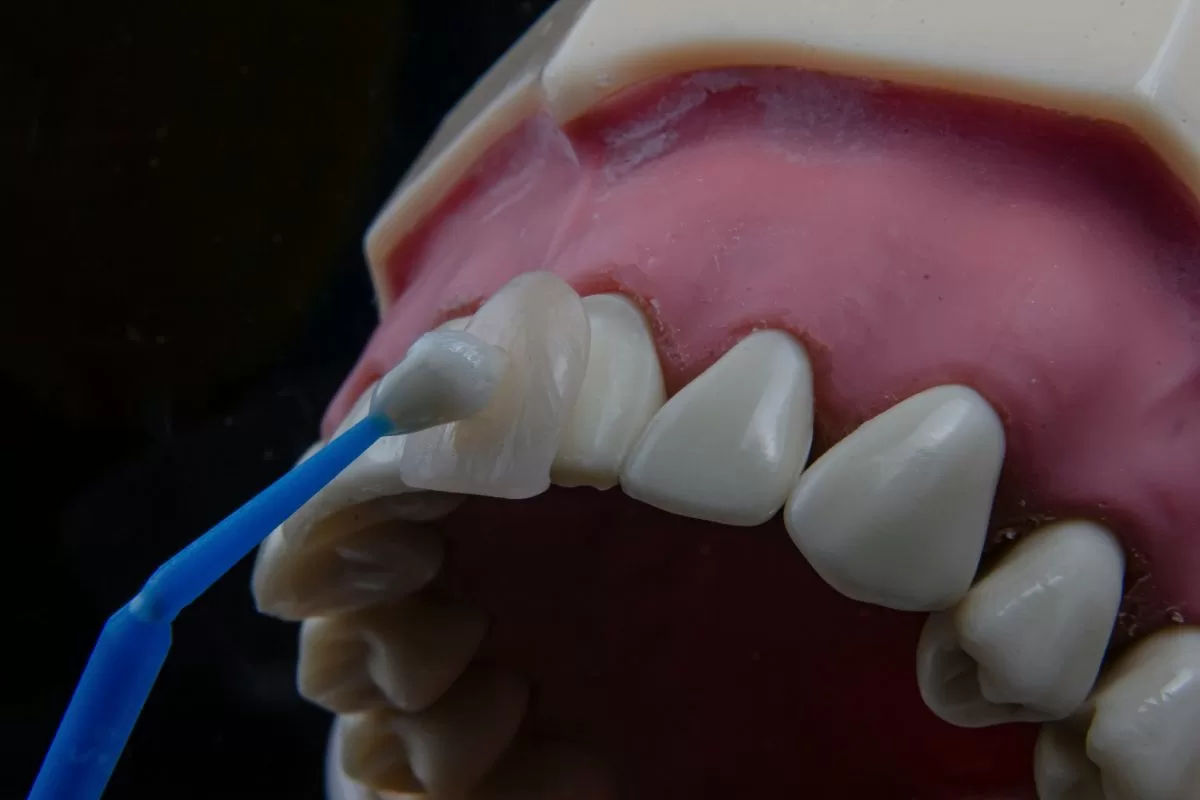
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It primarily involves inflammation and infection of the gums, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Understanding the various aspects of gum disease, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
Definition of Gum Disease
Gum disease is an inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not removed through proper oral hygiene, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to further complications. The two main stages of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the milder form, characterized by redness and swelling of the gums, while periodontitis is more severe and can result in tooth loss and damage to the bone supporting the teeth.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Understanding gum disease is essential, as it can have far-reaching effects not only on oral health but also on overall health. Research has shown links between gum disease and various systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. Therefore, recognizing the signs and symptoms early can lead to timely intervention and treatment.
Common Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease. Identifying these causes can help individuals take preventive measures to protect their oral health. Below are some of the most common causes associated with gum disease.
– Plaque Buildup
Plaque buildup is the primary cause of gum disease. It forms when bacteria in the mouth combine with food particles and saliva, creating a sticky film that adheres to the teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which is much more difficult to remove. Tartar can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and the onset of gingivitis.
To combat plaque buildup, it is essential to maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine. This includes brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth. Regular dental check-ups are also vital, as dental professionals can perform cleanings to remove tartar that has accumulated over time.
– Tobacco Use
Tobacco use is another significant risk factor for gum disease. Smoking and chewing tobacco can impair blood flow to the gums, making it more difficult for the body to heal and fight infections. Additionally, tobacco products can lead to a decrease in saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles and bacteria.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Quitting tobacco can have immediate and long-term benefits for oral health. Individuals who stop using tobacco products often notice improvements in their gum health, including reduced inflammation and bleeding. Support groups and cessation programs can provide valuable resources for those looking to quit.
– Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can also contribute to the development of gum disease. Fluctuations in hormone levels during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to inflammation. For instance, during pregnancy, increased levels of progesterone can enhance the response of the gums to plaque, leading to pregnancy gingivitis.
Women experiencing hormonal changes should pay extra attention to their oral hygiene during these times. Regular dental visits and open communication with dental professionals about any changes in gum health can help manage and mitigate the effects of hormonal fluctuations on oral health.
– Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition can play a significant role in an individual’s susceptibility to gum disease. Some people may inherit a tendency to develop gum disease due to their genetic makeup, which can affect immune response and inflammatory processes. If a family history of gum disease exists, it is crucial to be proactive about oral health and seek regular dental care.
Genetic testing is available for those who wish to understand their risk factors better. Knowing one’s genetic predisposition can empower individuals to take preventive measures and engage in more rigorous oral hygiene practices.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
– Poor Nutrition
Poor nutrition can significantly impact gum health. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums. Nutrients such as vitamin C, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids are vital for maintaining healthy gums and supporting overall oral health.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help strengthen gum tissue and reduce the risk of gum disease. Additionally, staying hydrated is essential for maintaining saliva production, which plays a crucial role in oral health.
Symptoms Overview
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease is essential for early intervention and treatment. The following are some of the most common signs that may indicate the presence of gum disease.
a) Gum Inflammation
One of the earliest signs of gum disease is inflammation of the gums, which may appear red, swollen, and tender. This condition, known as gingivitis, is often reversible with proper oral hygiene. However, if left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
Individuals experiencing gum inflammation should be vigilant about their oral care routine. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings can help reduce inflammation and restore gum health.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
b) Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums, particularly during brushing or flossing, is another common symptom of gum disease. This bleeding occurs due to the irritation and inflammation of the gum tissue caused by plaque buildup. If bleeding persists, it is crucial to consult a dental professional for evaluation and treatment.
Addressing bleeding gums early can prevent the progression of gum disease. Individuals should avoid aggressive brushing techniques, which can exacerbate the issue, and instead focus on gentle yet effective cleaning methods.
c) Bad Breath
Chronic bad breath, or halitosis, can be a sign of gum disease. The presence of bacteria in the mouth, particularly in areas where plaque has accumulated, can produce foul-smelling compounds. If bad breath persists despite regular oral hygiene practices, it may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, can help combat bad breath. However, if the problem continues, seeking professional dental advice is essential to address any potential gum disease.
d) Receding Gums
Receding gums occur when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s surface and potentially leading to tooth sensitivity and decay. This condition can be a sign of advanced gum disease and should be addressed promptly to prevent further complications.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Individuals experiencing receding gums should consult with a dental professional for evaluation and treatment options. Early intervention can help preserve gum tissue and prevent tooth loss.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. Various options are available, ranging from professional dental cleanings to surgical interventions. Below are some common treatment options for managing gum disease.
– Professional Cleanings
Professional dental cleanings are essential for maintaining gum health and preventing the progression of gum disease. During a cleaning, a dental hygienist removes plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and gums, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
It is generally recommended to schedule professional cleanings every six months, although individuals with gum disease may require more frequent visits. Regular cleanings can help keep gum disease at bay and ensure optimal oral health.
– Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure used to treat moderate to severe gum disease. This treatment involves the removal of plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing the roots of the teeth to promote healing and reattachment of the gum tissue.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Scaling and root planing may require local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort. Following the procedure, individuals may experience some sensitivity, but this typically subsides as the gums heal. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and ensure effective treatment.
– Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control bacterial infections associated with gum disease. These medications can be administered orally or applied directly to the affected areas. Antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and promote healing, particularly in conjunction with other treatment options.
It is important to follow the prescribed course of antibiotics and complete the treatment as directed. Individuals should also discuss any concerns or side effects with their dental professional.
– Surgical Treatments
For advanced cases of gum disease, surgical treatments may be necessary. Procedures such as flap surgery or bone grafting can help restore gum and bone health. Flap surgery involves lifting the gums to remove tartar and bacteria, while bone grafting can help regenerate lost bone tissue.
These surgical interventions are typically reserved for severe cases where non-surgical treatments have not been effective. A dental professional will assess the situation and recommend the most appropriate course of action based on individual needs.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Home Care Practices
In addition to professional treatments, maintaining a diligent home care routine is crucial for preventing and managing gum disease. The following practices can help promote healthy gums and overall oral health.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are vital for monitoring oral health and catching any potential issues early. During these visits, dental professionals can assess gum health, provide cleanings, and offer personalized recommendations for maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
Individuals should not wait until they experience symptoms to schedule dental appointments. Proactive care can help prevent gum disease and ensure a healthy smile for years to come.
Proper Brushing Techniques
Using proper brushing techniques is essential for effective plaque removal and gum health. Individuals should use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, brushing at a 45-degree angle to the gum line. Gentle, circular motions are recommended to avoid damaging the gum tissue.
Brushing should be done for at least two minutes, twice a day. It is also important to replace toothbrushes every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Flossing Importance
Flossing is a critical component of oral hygiene that is often overlooked. It helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gum line, areas that a toothbrush may not reach effectively. Daily flossing can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and promote overall oral health.
Individuals should use about 18 inches of dental floss, wrapping it around the middle fingers and using a gentle sawing motion to clean between the teeth. It is essential to be gentle to avoid damaging the gums.
Mouthwash Use
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can provide additional protection against gum disease. Mouthwash helps reduce plaque, fight bacteria, and freshen breath. It is important to choose a mouthwash specifically formulated for gum health and to follow the instructions on the label.
Mouthwash should be used as a complement to brushing and flossing, not as a substitute. Incorporating mouthwash into a daily oral care routine can enhance overall gum health and contribute to a brighter smile.
In conclusion, understanding gum disease is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this common condition. Regular dental visits, proper home care practices, and a commitment to oral hygiene can lead to healthier gums and a brighter smile.
Don't Delay Your Treatment
Let's create your personalised treatment plan right away with a complimentary consultation with our specialist dentists.
Secure Your Healthy Smile with Genç Dental
Don’t let gum disease compromise your smile. At Genç Dental®, we understand the importance of comprehensive oral care. Our team of specialist physicians and academic-minded doctors are dedicated to providing top-notch services to ensure your gums stay healthy and your smile stays bright. With our commitment to cutting-edge treatments and patient education, we’re here to support you every step of the way. Contact us today to schedule your appointment and take the first step towards optimal oral health.